Terms You Need to Know
In order to properly explain how thermal paste functions, it’s worth defining some of the terms we will be using.
Central Processing Unit (CPU) - The information processing center of a PC. It executes all operational instructions and sends instructions to the other hardware in the computer. If the computer is a body, then the CPU is the brain, and it is absolutely critical to the functioning of any PC. Modern CPUs execute a high volume of operations per second, and this generates heat. In order for a CPU to operate at peak efficiency, it needs to be properly cooled, usually with a cooling apparatus designed just for this purpose. This is where thermal paste becomes important. If you'd like to learn more about how a CPU is made, you can read more about the manufacturing process.
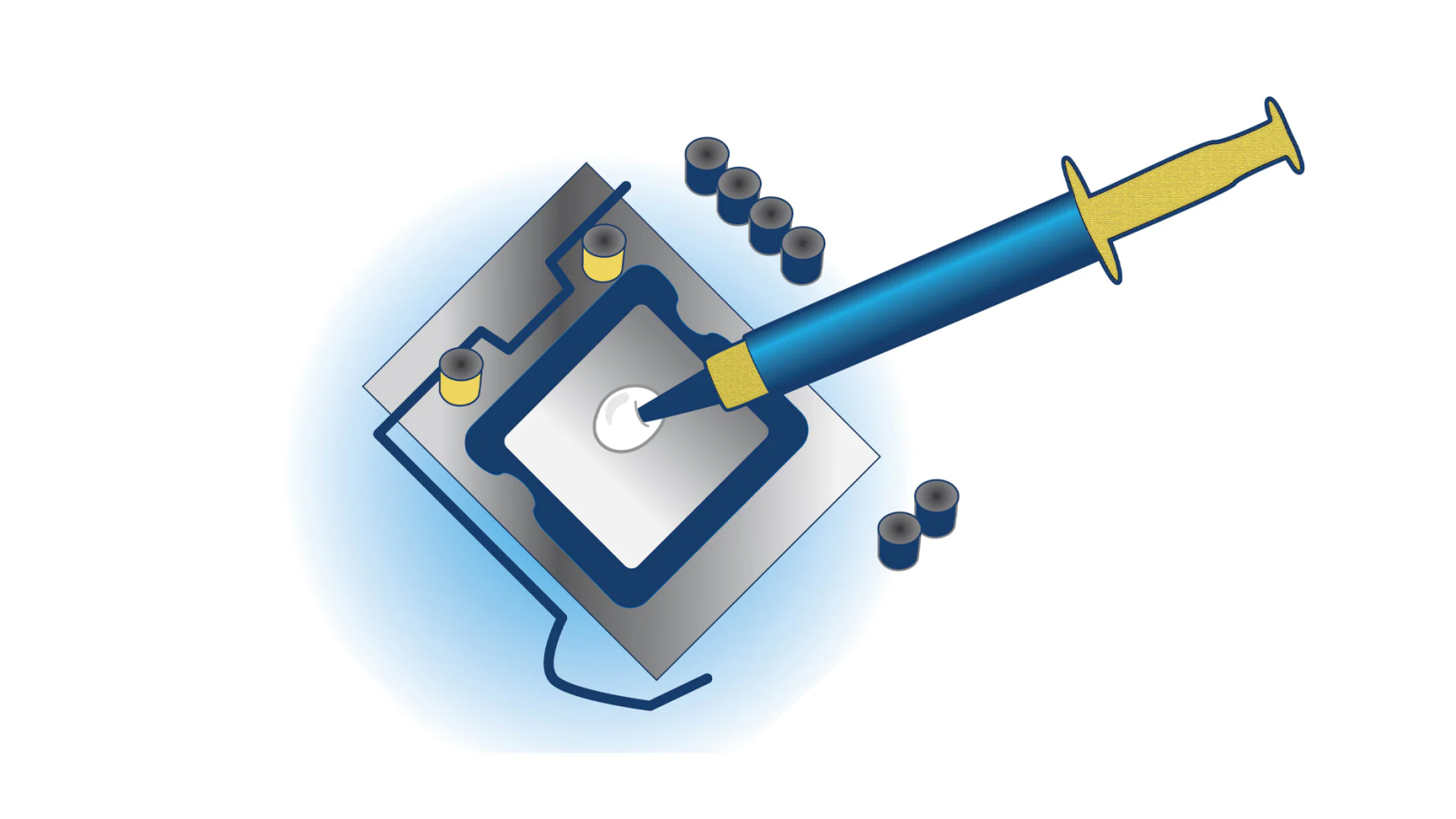
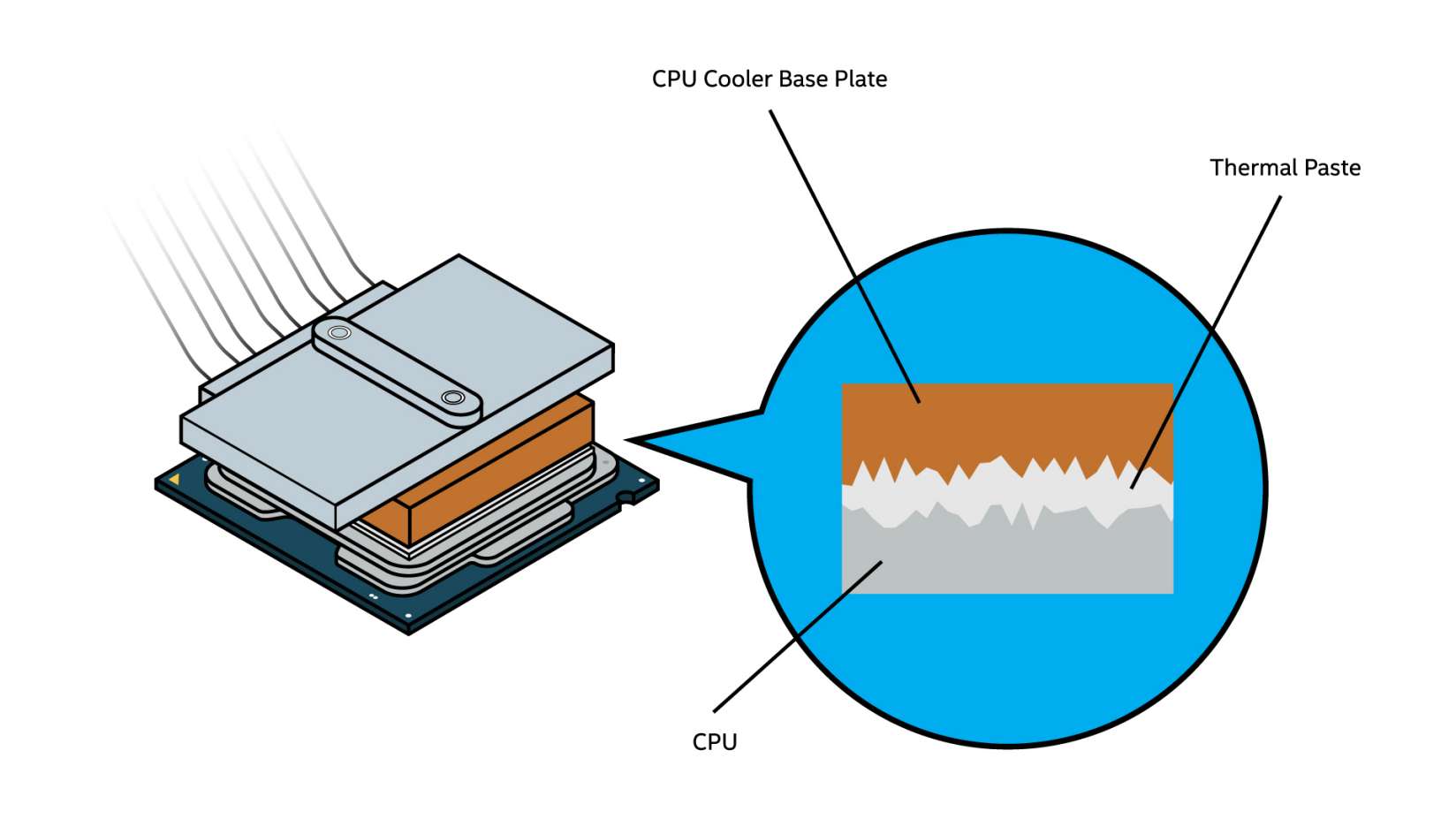
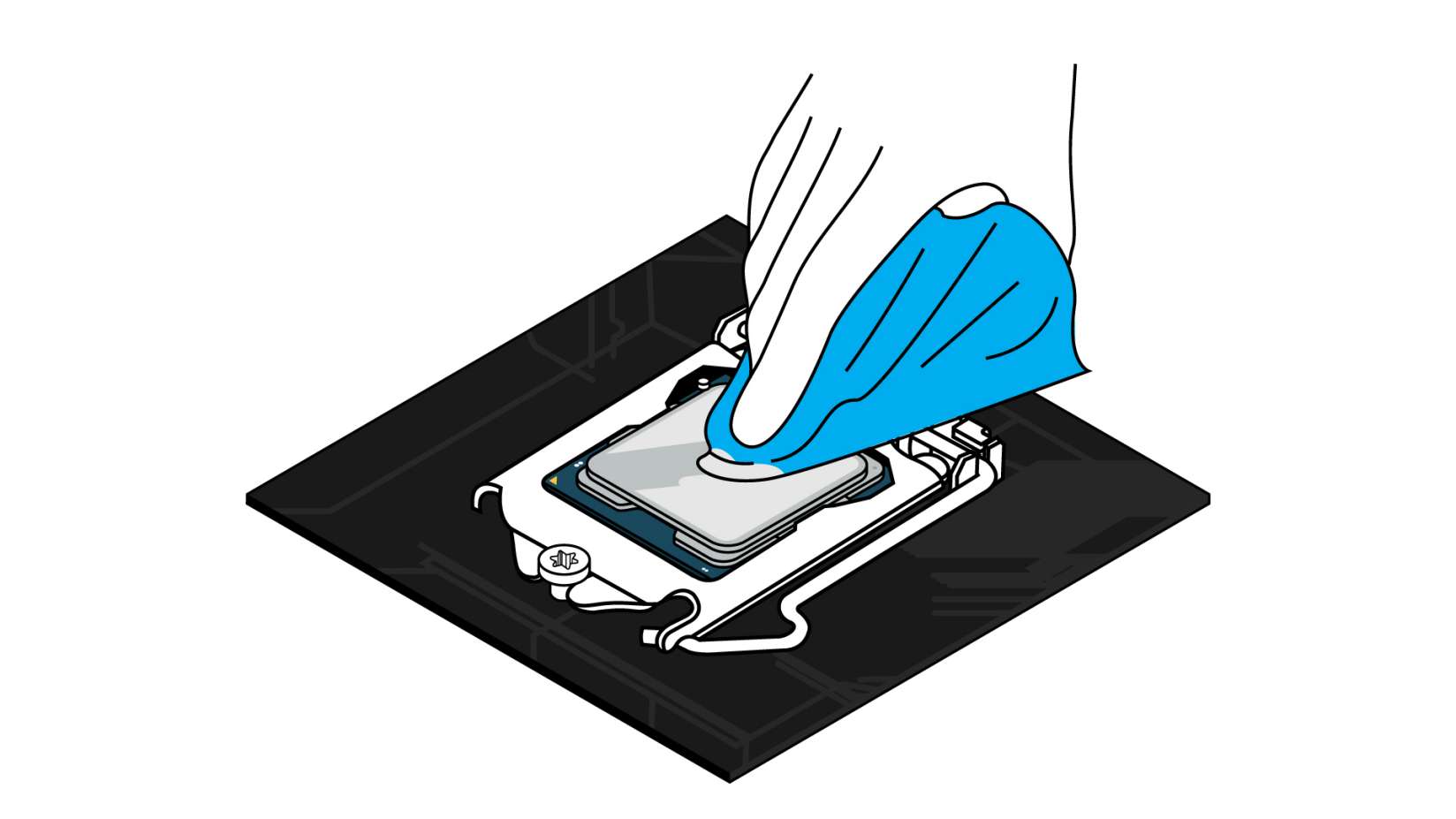
Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS) - The metal “lid” of the CPU. This serves as a heat sink designed to distribute heat from the processor itself to a CPU cooler, as well as provide protection to the processor inside. This is the part of the CPU that is still exposed after being installed in a motherboard, and is the surface to which you apply thermal paste.
CPU Cooler - The device that keeps your CPU running at optimal temperatures. CPU coolers usually use air or liquid to relocate the heat created by the operation of the CPU.
Base-Plate - The metal base of an air-cooler that attaches to the IHS of the CPU. This design allows the transfer of heat through convection to the fins of the heat sink, where it can then be redistributed with a fan.
Waterblock - The apparatus that attaches to the IHS when using an All-in-One (AIO) liquid cooler or a custom cooling loop. It transfers heat from the IHS to the heat transfer fluid, which then relocates that heat to be redistributed by fans at a radiator.
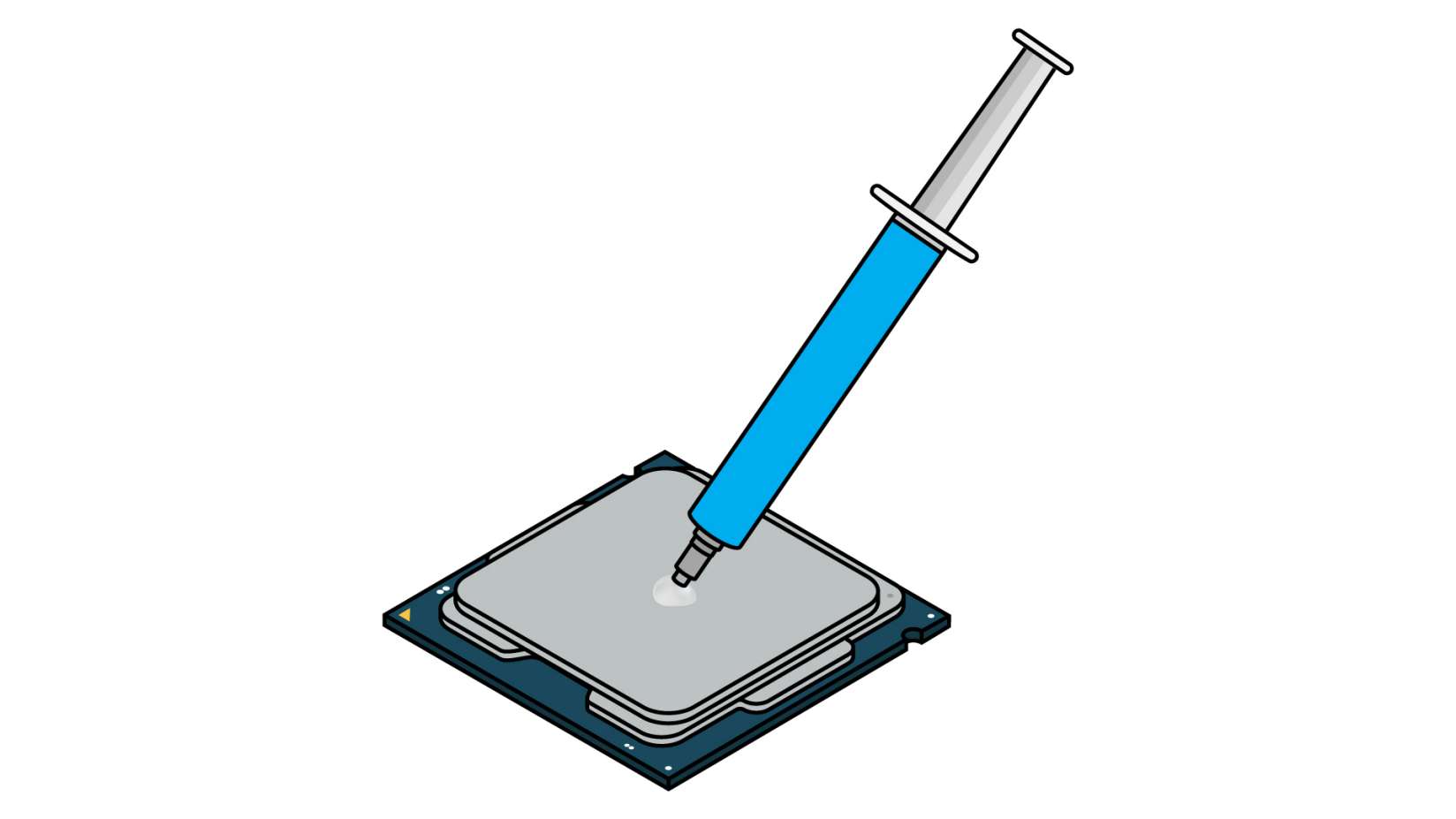
Thermal Paste - A silvery-gray substance that you apply to a processor before installing a cooling solution. It allows for an efficient transfer of heat from the IHS of the processor to the base plate or water block of the CPU cooler that is designed to dissipate that heat.